Research on unsaturated porous media
Our research on unsaturated porous media had experimental and theoretical activities. Experiments focused on the inertial phase of imbibition into porous media. Our theoretical work exploited statistical mechanics to predict the retention behavior of unsaturated porous media from known surface energy and pore geometry. We also used the statistical mechanics to elucidate the behavior of the hysteretic gas-solid-liquid triple contact line with or without electrowetting, as outlined below.
Experiments on the International Space Station
On December 10 at 5:30am EST, ISS Commander Luca Parmitano successfully set up ISPS hardware in the Microgravity Science Glovebox of the International Space Station, while Zin-Tech engineers Cathy Frey and Ryan Martz communicated with Cdr Parmitano in the Telescience Support Center of the NASA-Glenn Research Center. Shilpa Sahoo and Michel Louge monitored operations from the TSC, while Anthony Reeves did so remotely from Cornell. Operations with water drops took place on December 11. A live stream of the experiment was available on NASA-TV. This article in the Cornell Chronicle provides additional context.


The goal of the ISPS was to observe the imbibition of water into well-characterized cylindrical capillaries on time and length scales long enough to observe details hitherto inaccessible under Earth gravity. The data set can be used as a benchmark for validating numerical simulations on complex capillary geometry.
The principal results of the experiments and their interpretation are found in the thesis of Shilpa Sahoo. Data and analysis of the ISS microgravity experiments are available to the public on stable DOIs for preparation and experiment design, video data, and data reduction and analysis .
A summary of the principal ideas follow.
When a drop touches a porous medium, it spreads as if laid on a composite surface. The surface first behaves as a hydrophobic material, as liquid must penetrate pores filled with air. When contact is established, some of the liquid is drawn into pores by a capillarity that is resisted by viscous forces growing with length of the imbibed region. This process always begins with an inertial regime that is complicated by the motion and possible pinning of gas-liquid-solid contact lines jumping over newly-wetted capillaries. A question is whether simulations can capture such crucial subtleties.
To study imbibition on Earth, time and distance must be shrunk to mitigate gravity-induced distortion. These small scales make it impossible to observe inertial and pinning processes in detail. Instead, our rig, which was designed by Zin-Tech, a NASA contractor, slowly extruded water spheres until they touched the capillary plate. Their 12mm diameter were large enough to visualize details near individual capillaries, and long enough to observe dynamics of the entire imbibition process. To investigate the role of contact pinning, we used several kinds of porous capillary plates made of metal treated with Self-Assembled Monolayers (SAM), thereby fixing advancing and receding contact angles at known values. These detailed observations will eventually serve as benchmark for numerical simulations.
A visual text matrix of still frames for each of our nine experiments is below.
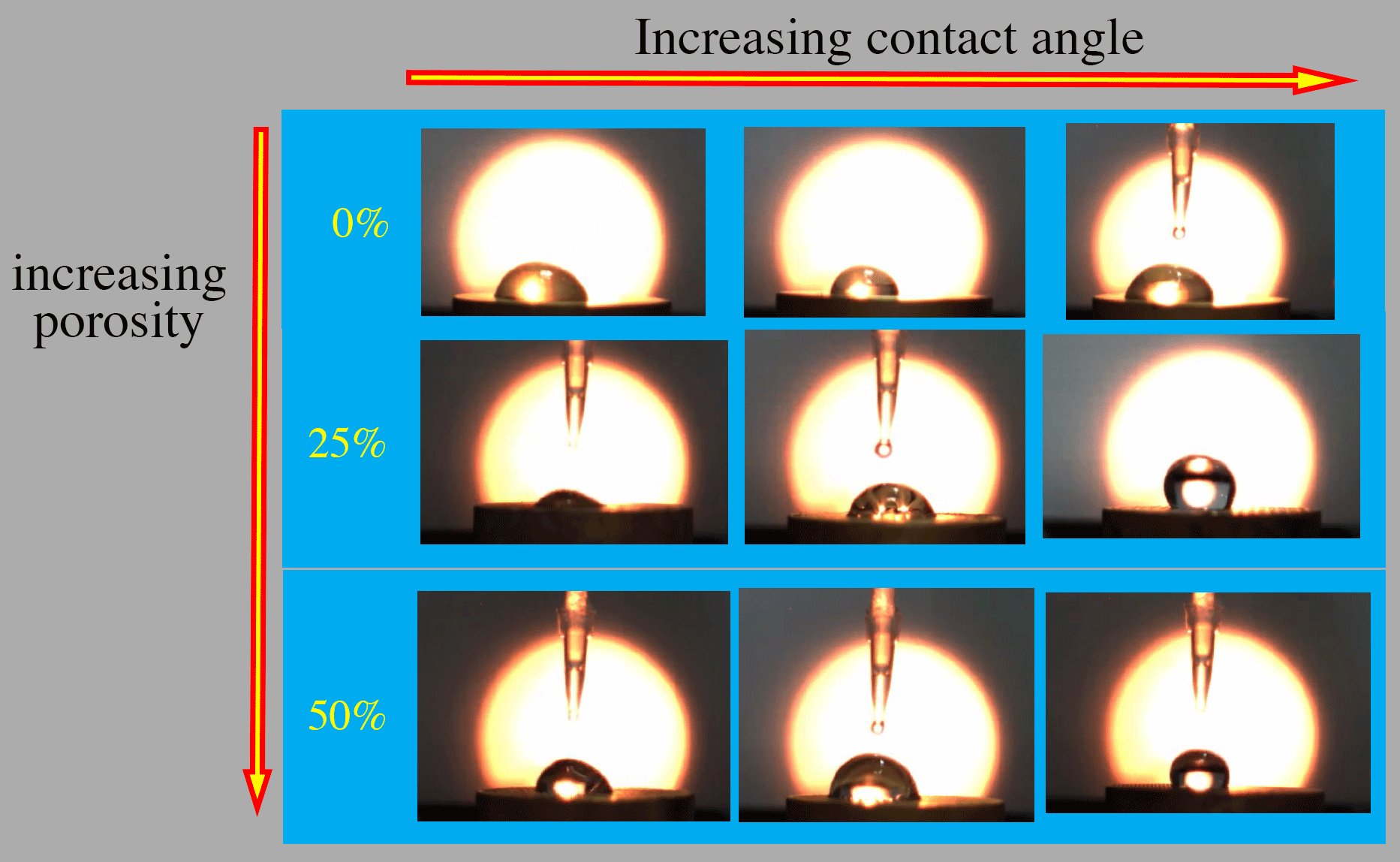
We designed capillary plates with different porosity densities and different contact angles. Nominal plate dimensions are 3D x 1.5D, with D at least 12mm. At the largest surface density of 50%, the clearance between adjacent holes must be kept as large as possible to ensure maximum strength. Therefore, cylindrical capillaries are arranged on a triangular lattice. Two different porosities of 50% and 25% were staged on a triangular/hexagonal-packing as shown below. The brass capillary plates were manufactured by Zin-Tech to the desired specifications.

Capillary plates made of metal must first be coated with a thin layer of gold by electroplating after the metal plate has been machined to the required roughness. Because SAM is stable on gold but rarely on other metals, gold plating must first be applied. The challenge is that traditional electroplating cannot penetrate small capillaries. Instead, Professor Sadik Omowunmi and her students Ezer Castillo and Roland Miller at the University of Binghamton developed a new method of electroless plating for this application. Doing so, they gold-plated nine brass samples.
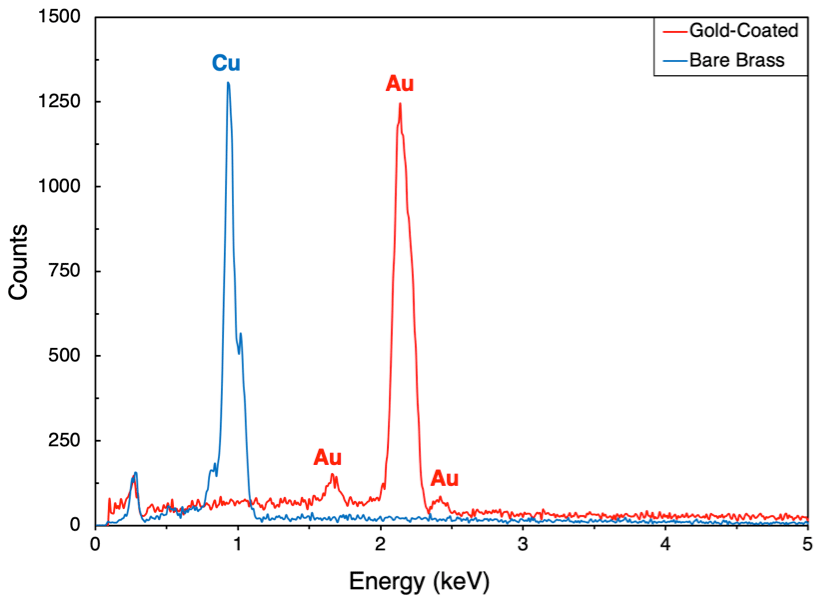
Professor Omowunmi and her students used a Zeiss FE-Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Supra-55 VP to image the surface of the brass plates before and after gold-coating (see below). The gold-coating was evident as seen from the cauliflower-like globular gold particles.

Professor Omowunmi and her students also analyzed the elemental composition of the samples by energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). This was done using an EDS detector in the SEM (figure below).
All gold-covered plates were then coated with Self-Assembled-Monolayers (SAM) in Professor Susan Daniel’s lab as shown below. Thiols 6-Mercapto-1-Hexanol, 6-Mercaptohexanoic Acid 90% and 8-Mercaptooctanoic Acid 95% were used. The corresponding contact angles and their hysteresis were measured in CNF’s Rame 500 Goniometer. We found hydrophilic angles of 26°, 46° and 68° for 6-Mercapto-1-Hexanol, 6-Mercaptohexanoic Acid 90% and 8-Mercaptooctanoic Acid 95% respectively.

A crucial requirement of ISPS was to extrude a droplet of diameter 12 mm and observe its spreading and imbibition. To that end, Zin-Tech used a manual repetitive pipette from Brandtech. They selected a hydrophobic tip to prevent water from climbing toward the pipette in microgravity. They tested the tip behavior on parabolic flights of NASA's KC-135 A, operated by the Reduced Gravity Office of the NASA Johnson Space Center (picture below).
Brandon Kirkman extrudes a spherical water drop through a hydrophobic pipette tip.
Ryan Martz and Brandon Kirkman of Zin-Tech conducted tests of camera objectives for the Prosilica GX1050C in the ground-based mockup of the Microgravity Science Glovebox at the Marshall Space Flight Center (below). A glass marble was used to simulate the water sphere.
Earlier imbibition experiments in ground-based facilities
In collaboration with Jonathan Kollmer, Thorten Poschel and their students at the University of Erlangen
(Germany) and colleagues at CentraleSupelec near Paris (France), we developed a microgravity experiment to elucidate the
onset of imbibition of a wetting liquid in cylindrical capillary tubes,
which is dominated by liquid inertia. As this high-speed movie shows,
our prototype of the free-fall apparatus created a relatively large
stable sphere of water that was brought in contact with a plate where
capillaries were drilled. The experiment is meant to test the
Lattice-Boltzmann simulations of Frank and Perre (2012) and Frank, Perre and Li (2015). In this project, we work with authors of the simulations at CentraleSupelec and the IATE group at INRA-CIRAD-UMII-SupAgro in Montpellier (France).
Once a relatively large stable
water sphere of 14mm diameter is created, a plate with cylindrical
capillaries is brought to meet it and begin the imbibition process.
This experiment lasted less than a second as high-speed camera and
apparatus were dropped from the ceiling in our lab to a padded
container below (movie by Carlos Mejia, Doug Berman, John Bartlett and Richard Goodwyn).

The Cornell team: (Left composite,
clockwise from
upper left) Carlos Mejia, Douglas Berman, John Bartlett, Nicole Panega,
Derek Paxson, Gilbert Hegermiller, Rukang Huang. In the selfie: John
Bartlett, Carlos Mejia, Douglas Berman and Richard (Blake) Goodwyn.
(Right) May 2015 graduation picture with Rebecca Jung, Gil Hegermiller,
Michel Louge, Rukang Huang and Nicole Panega.
Our collaborators at the University of Erlangen improved the clam-shell release mechanism for tests at the ZARM drop tower
in Bremen (Germany) in November 2015, under the aegis of the European Space Agency Educational Office. Top left: Laura Steub and
Florian Fuchs pose in front of their creation. Right: the four
identical clam-shells to be dropped. Bottom left: the structured porous plates to be
tested. Electronic controls were designed by Achim Sack.
From left to right and top to
bottom: Douglas Berman, Laura Steub, Florian Fuchs, Jonathan Kollmer
and John Bartlett assemble one the four clam-shells. The payload is
ready to place in the drop capsule. The Erlangen-Cornell team poses in
front of the ZARM microgravity drop tower
with inset showing the clam-shell assembly. John Bartlett examines the
magnetic release of the clam shell. Laura Steub and John Bartlett
assemble the system in the payload. Joel Casalinho (CentraleSupelec)
looks on while John Bartlett and Douglas Berman review the capsule
telemetry. Photos: M. Louge and J. Kollmer.

From left to right and top to
bottom: Nigel Savage (ESA Education), Achim Sack, and Jonathan Kollmer
(Erlangen) test the imaging system with full illumination. Thorsten
Poschel, Achim Sack and Jonathan Kollmer review telemetry while Laura
Steub prepares porous samples. Douglas Berman (Cornell) coats a
clam-shell with hydrophobic material. Joachim Sack prepares the
electronics. Herve Duval (CentraleSupelec) and Jonathan Kollmer discuss
spreading and imbibition models. Lily Ha (ESA) and Nigel Savage look on
as Jonathan Kollmer assembles the actuator system. Laura Steub and
Jonathan Kollmer inspect the payload. Photos: Michel Louge.
"Dropping Drops", movie prepared by Nigel Savage of ESA Education, reproduced by permission.
The article below for the Powders and Grains 2017 conference summarizes results of the Bremen microgravity campaign at the ZARM free-fall tower in November 2015.
Laura Steub, Jonathan
Kollmer, Derek Paxson, Achim Sack, Thorsten Poschel, John Bartlett,
Douglas Berman, Yaateh Richardson, and Michel Y. Louge, Microgravity spreading of water spheres on hydrophobic capillary plates, Powders and Grains 2017 - 8th International Conference on Micromechanics on Granular Media, F. Radjai, ed., http://www.epj-conferences.org/, EPJ Web of Conferences 140, 16001 (2017) ISSN:2100-014X, doi: 10.1051/epjconf/201714016001.
We created nearly perfect centimetric spheres of water by splitting a cavity consisting of two metal hemispheres coated with a hydrophobic paint and under-filled with liquid, while releasing the apparatus in free-fall. A high-speed camera captured how water spread on hydrophobic aluminum and polycarbonate plates perforated with cylindrical capillaries. We compare observations at the ZARM drop tower in Bremen with Lattice-Boltzmann numerical simulations of Frank, Perre and Li for the inertial phase of imbibition.
Theory
As explained in the paper below, we introduced a new theoretical framework based on statistical mechanics to predict the "retention curve" charting the degree of saturation of a porous vs capillary pressure. The theory attributes hysteresis in this curve to first-order phase transitions in the void network. We also attribute Haines jumps to viscous dissipation of the corresponding latent energy of transition. This project is a collaboration with the 3SR laboratory (Grenoble, France), IFSTTAR (Universite de Nantes) and Maersk Oil in Qatar.
Jin Xu and Michel Y. Louge: “Statistical Mechanics of Unsaturated Porous Media”, Phys. Rev E 92, 062405 (2015).
We explore a mean-field theory of fluid imbibition and drainage through permeable porous solids. In the limit of vanishing inertial and viscous forces, the theory predicts the hysteretic "retention curves" relating the capillary pressure applied across a connected domain to its degree of saturation in wetting fluid, in terms of known surface energies and void space geometry. To avoid complicated calculations, we adopt the simplest statistical mechanics, in which a pore interacts with its neighbors through narrow openings called "necks", while being either full or empty of wetting fluid. We show how the main retention curves can be calculated from the statistical distribution of two dimensionless parameters measuring the specific areas of neck cross-section and wettable pore surface relative to pore volume. The theory attributes hysteresis of these curves to collective first-order phase transitions. We illustrate predictions with a porous domain consisting of a random packing of spheres, show that hysteresis strength grows with specific neck area and weakens as the distribution of specific wettable pore area broadens, and we reproduce the behavior of Haines jumps observed in recent experiments of Armstrong and Berg [Phys. Rev. E 2013] on an ordered pore network.
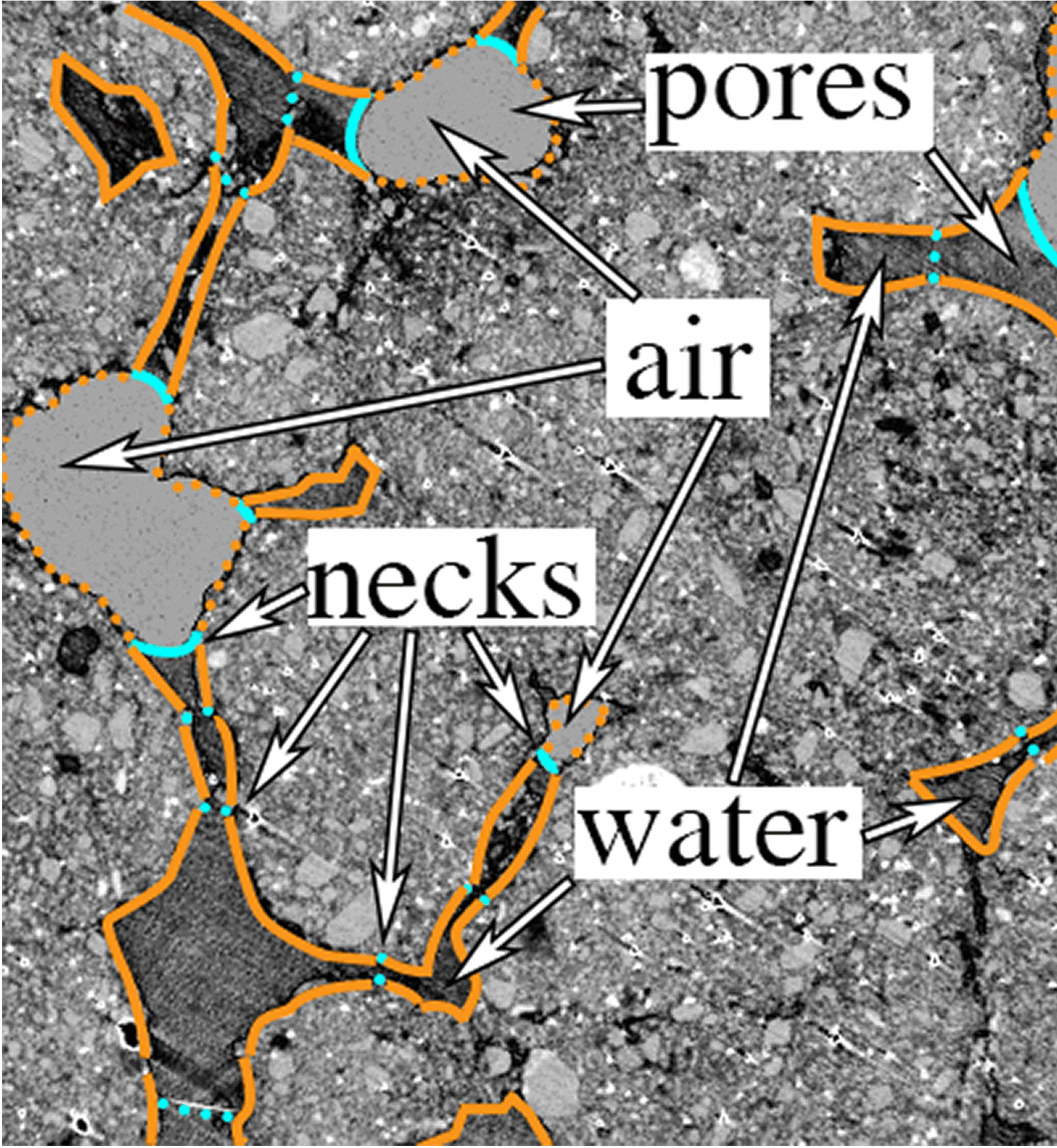
Tomography (CT) of an unsaturated porous soil aggregate, with superimposed qualitative identification of pore volumes, pore wettable surface area (orange) and neck area (blue). Continuous and dotted blue lines show, respectively, air-water interfaces and boundaries between two connected water-filled pores. Continuous and dotted orange lines mark, respectively, pore surface area in contact with water or air. (Photo courtesy Valerie Pot and Philippe Baveye).
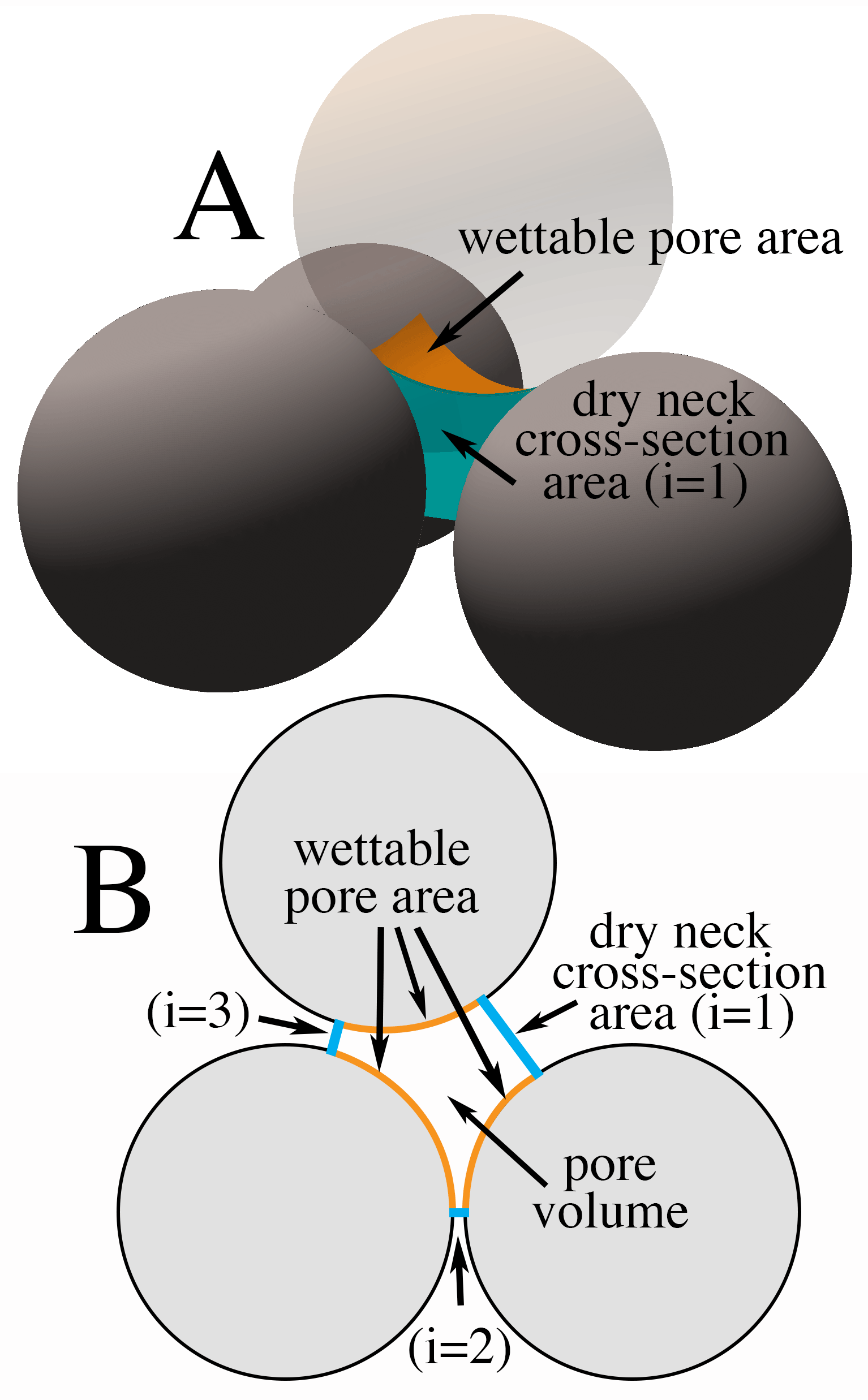
Pore geometry characterization illustrated with a packing of identical spheres. (A) Single pore wedged between an irregular tetrahedron of four spheres. The contribution of the top sphere to the pore surface area is highlighted in orange. Three spheres in the foreground delimit the dry neck cross-section of index (i=1) shown in blue. (B) Section through centers of the three darker spheres showing traces of three of the four dry neck cross-sectional area, wettable pore surface area, and pore volume. Sphere positions in the granular packing were calculated by Patrick Richard.
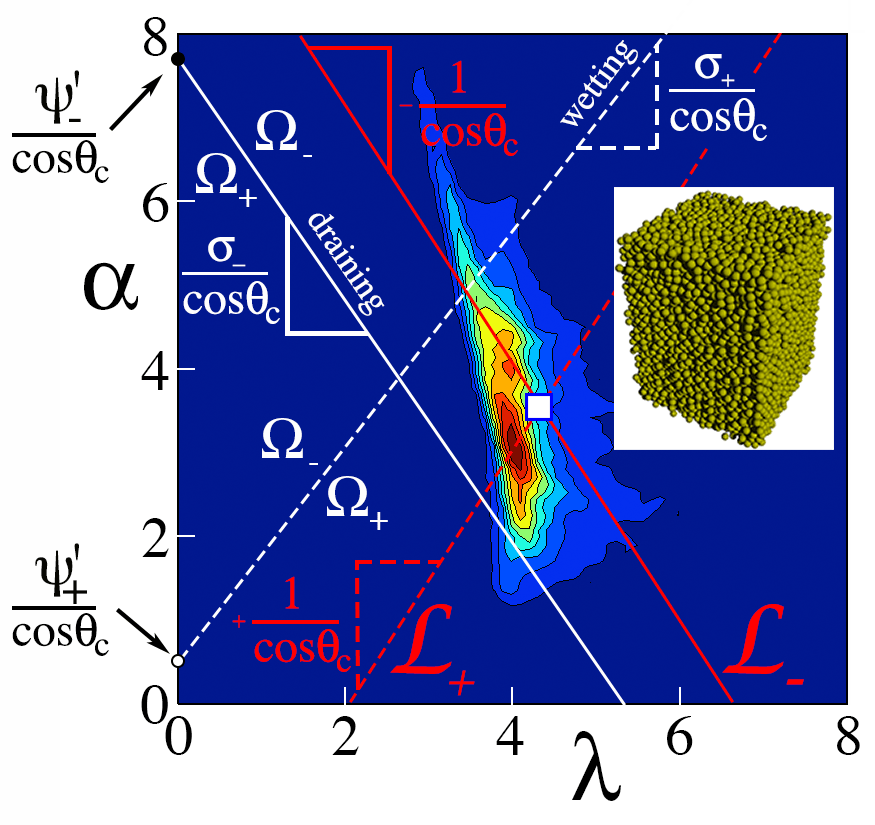
Contour plot of the distribution of specific neck cross-section lambda and specific wettable pore area alpha for the random packing shown in the inset. Symbols and details are in the paper above. The retention curve below is deduced from the "frozen disorder" contained in this distribution. Simulations were carried out by Patrick Richard. Lili Gu helped carry out the Delaunay triangulation to reduce the data.
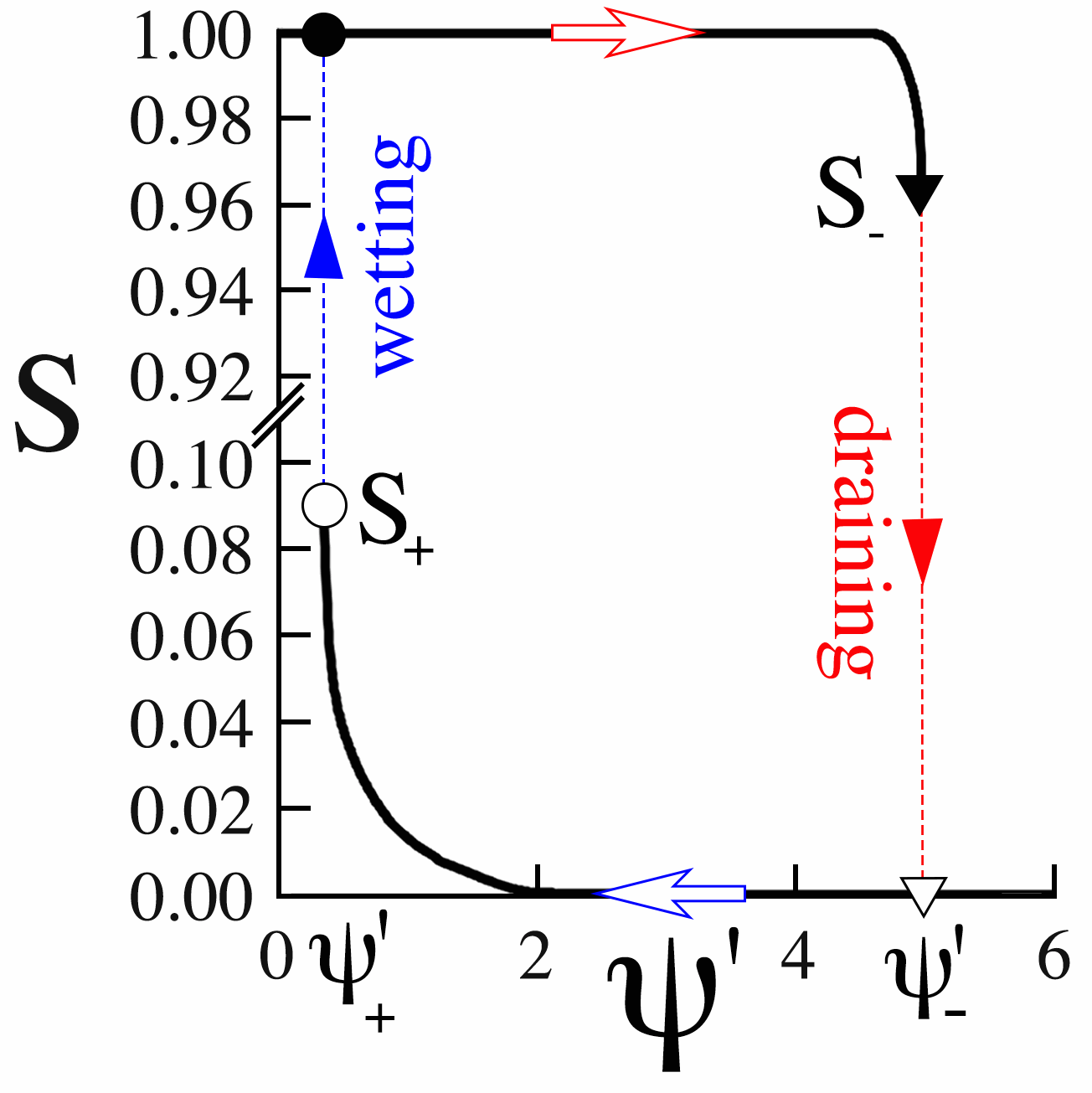
Imbibition and drainage retention curves charting degree of saturation vs dimensionless capillary pressure for the distribution above and a contact angle of 50°.
Follow this link to the thesis of Jin Xu, who was instrumental in developing the statistical mechanics theory mentioned above.
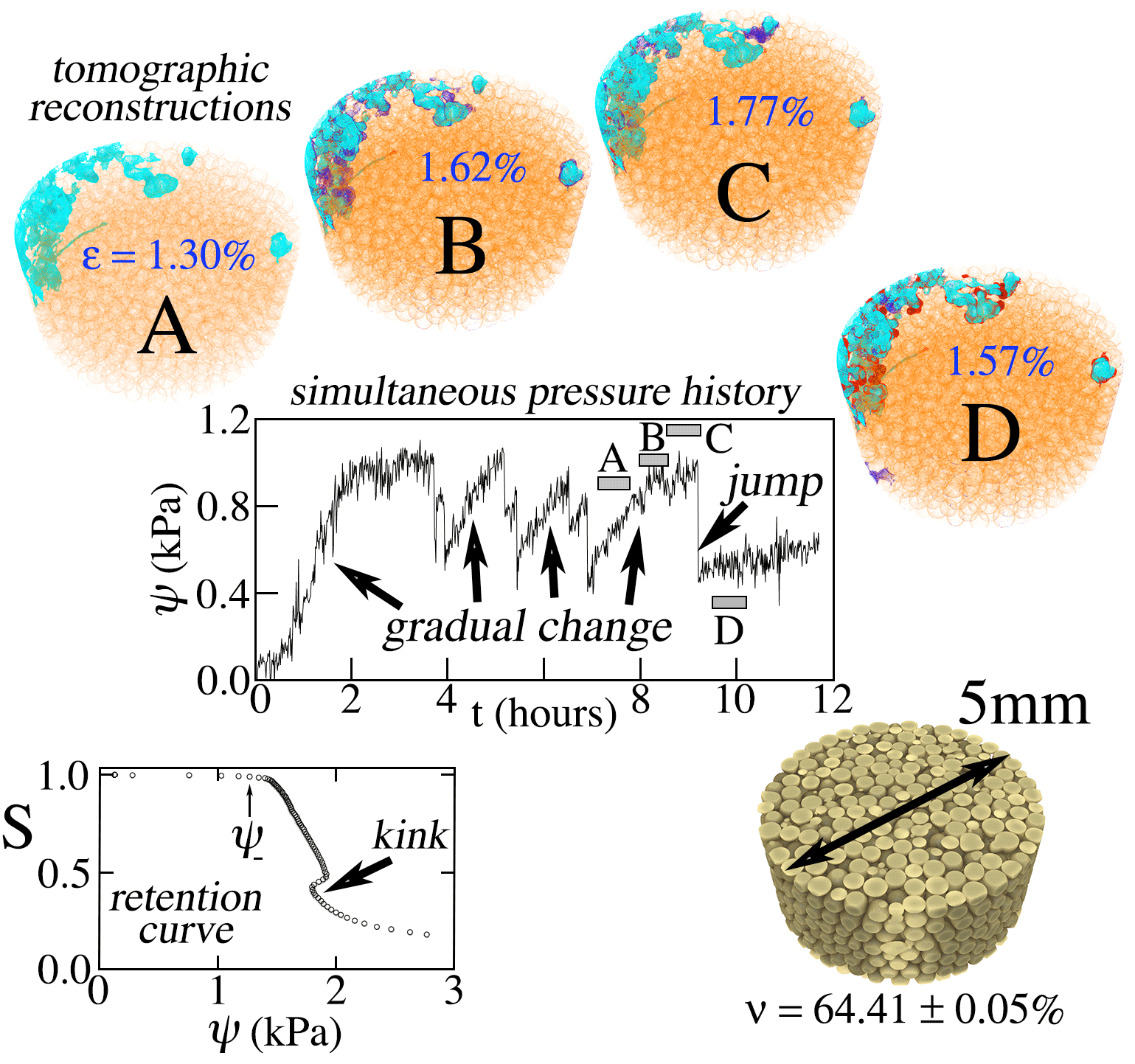
Jin Xu, Theis Solling, Thomas McKay and Michel Y. Louge: “Tension and tomographic measurements while draining water from a granular sample”, ICTAM-2016, Montreal.
We report simultaneous measurements of capillary pressure and water distribution in an unsaturated bed of glass beads subject to evaporation-induced drainage using xray computed tomography (CT) and a tensiometer. The data reveal that drainage can occur with or without pressure jumps. In the statistical mechanics framework of Xu and Louge [PRE 92:062405, 2015], these observations suggest that the drainage phase transition involves reversible periods punctuated by irreversible avalanches.
Michel Y. Louge: “Statistical mechanics of the triple contact line”, Phys. Rev. E 95, 032804, doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.95.032804 (2017).
We outline a statistical mechanics of the triple gas-solid-liquid contact line on a rough plane. The analysis regards the neighborhood of the line as a solid dotted with cavities. It adopts the simplest mean-field statistical mechanics, in which each cavity is either full or empty, while being connected to near-neighbors by thin necks. The theory predicts equilibrium angles for advance and recession in terms of the Young contact angle and the joint statistical distribution of two geometrical parameters representing specific neck cross-section and specific cavity opening. It attributes contact angle hysteresis to first-order phase transitions among adjacent cavities, as they collectively imbibe or reject liquid. It also calculates the potential energy barriers that hysteresis erects against overcoming contact line pinning. By determining whether the phase transitions can release latent energy, this ab initio analysis distinguishes six regimes, including two metastable recession states. Predictions compare well with data for superhydrophobia on microscopic rods (Gao and McCarthy, 2006; Lafuma and Quere, 2003); for hysteresis in the "Wenzel state" (Lam et al, 2002); for variations of the advancing contact angle with surface energies of the liquid (Shibuichi, et al, 1996), and for superhydrophobic "reentrant structures" (Liu and Kin, 2014).
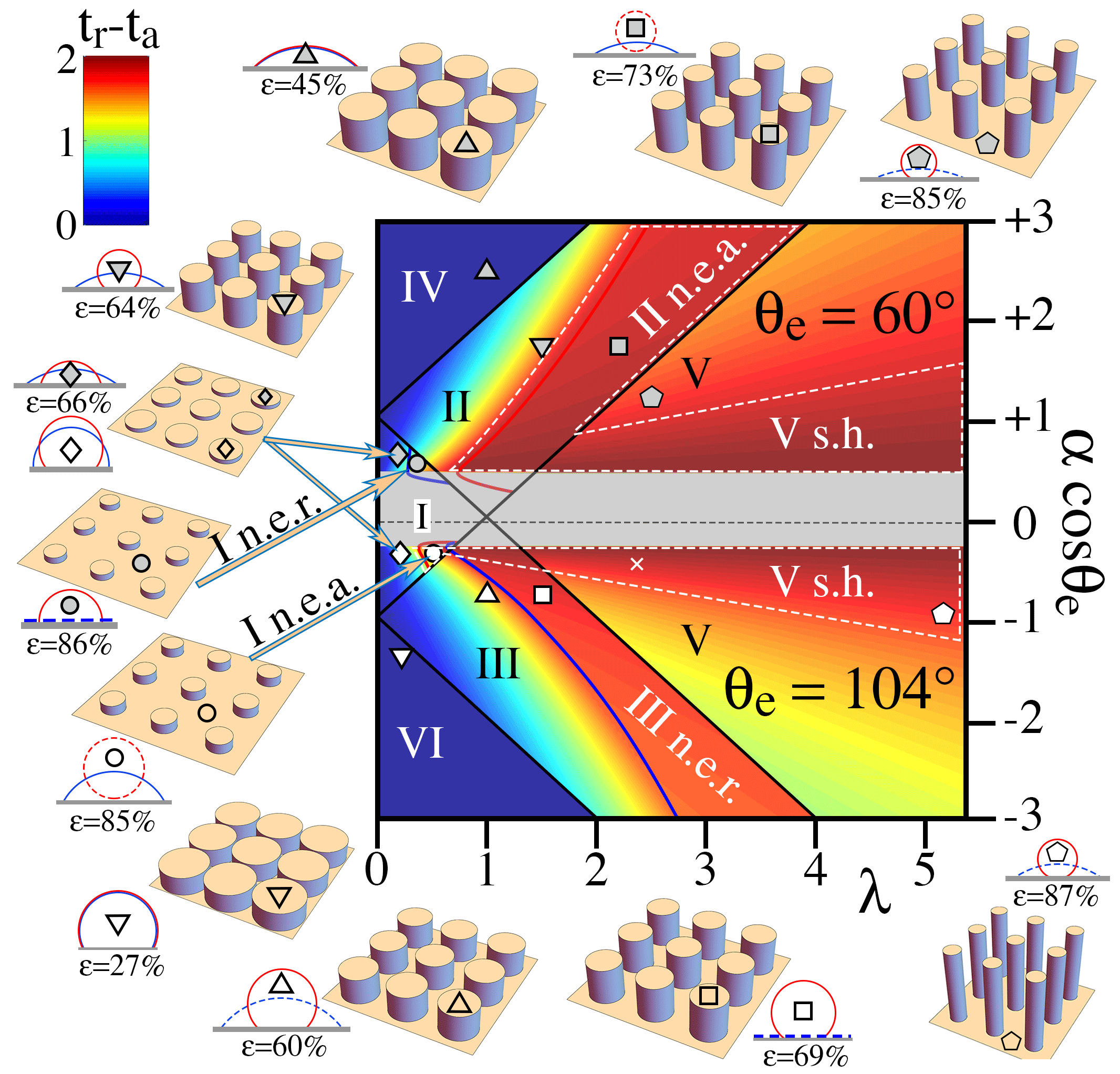
Phase diagram illustrating the six regimes predicted by the statistical mechanics. The abscissa is the specific cross-section of "necks" linking cavities on the surface. The ordinate is the specific wall area of these cavities, multiplied by the cosine of the Young contact angle on a flat plane of the same material without defects. Regions of non-equilibrium advancing (n.e.a.) contact are found in regimes I and II. Non-equilibrium receding (n.e.r.) contacts also exist in regimes I and III. White dashed lines surround superhydrophobic (s.h.) regions with contact angle > 150 deg in regimes I, II and V. Symbols are used to match positions in the diagram with sketches of the corresponding bed of rods and their spherical liquid caps for advancing (red) and receding (blue) contact angles; dashed blue caps denote metastable recession or n.e.r. states; dashed red caps are n.e.a. states. The white cross is the data of Lafuma and Quere (2003). The background color scale on the upper left shows hysteresis strength; at equilibrium, deep blue indicates no hysteresis; deep red maximum hysteresis.
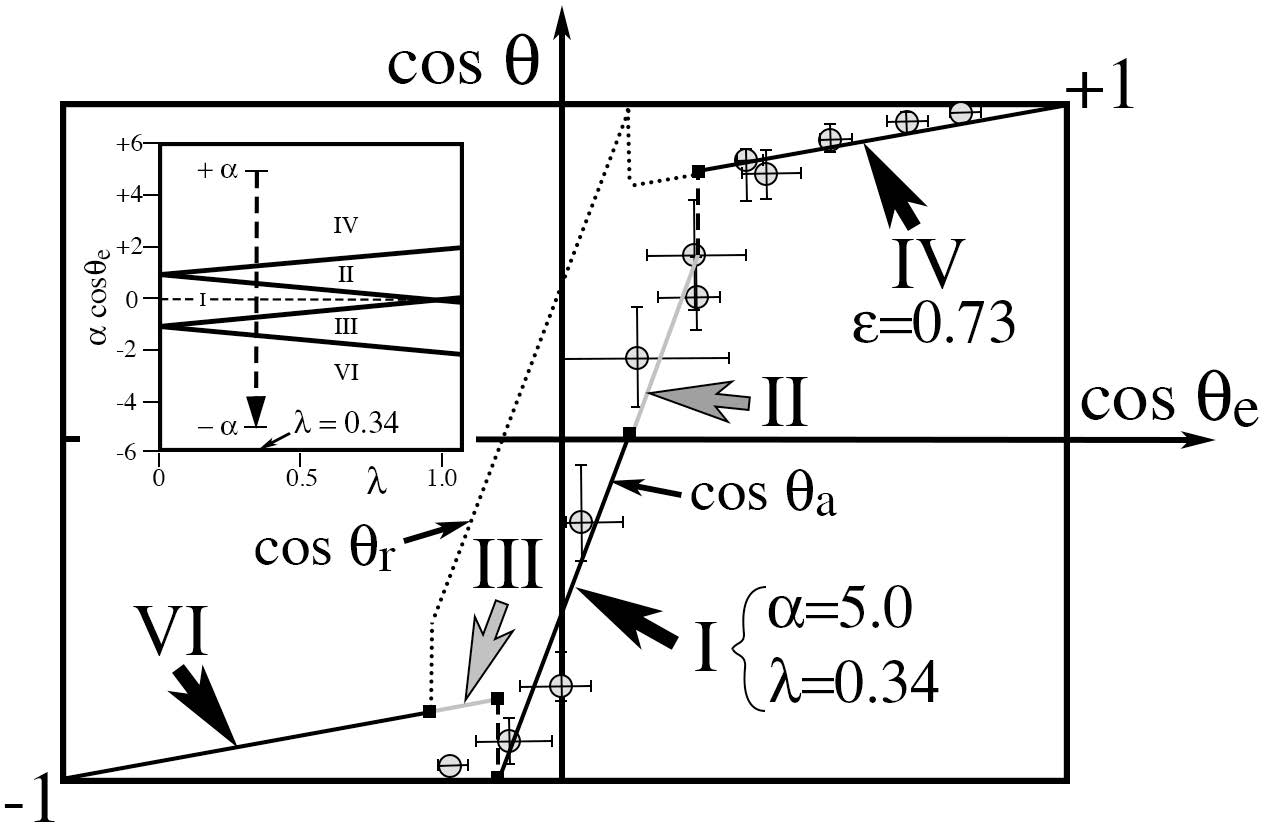
Cosine of advancing contact
angles of water and 1,4 dioxane liquid mixtures on fractal alkylketene
dimer surfaces vs cosine of the corresponding Young angles measured on
the same flat surfaces by Shibuishi, et al
(symbols). Solid lines are predictions of the model. Over the range of
cosines of the Young contact angle from highest to lowest (inset,
dashed arrow), we predict that the measured cosine of the advancing
angle successively explores regimes IV, II, I, III and VI in the
parameter space above. Changes in this cosine are smooth from II to I
and III to VI, but abrupt (dashed lines) from IV to II and I to III.
Data suggest a linear dependence of the advancing cosine that does not
pass through the origin. In our model, such offset is due to finite
specific neck areas.
Michel Y. Louge and Shilpa Sahoo: “Model of inertial spreading and imbibition of a liquid drop on a capillary plate”, AIChE J. 63, 5474-5481 (2017), doi:10.1002/aic.15953 .
We outline a low-order Lagrangian model for the inertial dynamics of spreading and imbibition of a spherical liquid cap on a plane featuring independent cylindrical capillaries without gravity. The analysis predicts the relative roles of radial and axial kinetic energy, reveals the critical Laplace number beyond which the drop oscillates, and attributes the exponent of the initial power-law for contact patch radius vs time to the form of capillary potential energy just after the liquid sphere touches the plate.
Louge, M.Y. and Wang, Y.: “Statistical Mechanics of Electrowetting”, Entropy, 26(4), p.276 (2024), doi:10.3390/e26040276 .
We derive the ab initio equilibrium statistical mechanics of the gas--liquid--solid contact angle on planar periodic, monodisperse, textured surfaces subject to electrowetting. To that end, we extend an earlier theory that predicts the advance or recession of the contact line amount to distinct first-order phase transitions of the filling state in the ensemble of nearby surface cavities. Upon calculating the individual capacitance of a cavity subject to the influence of its near neighbors, we show how hysteresis, which is manifested by different advancing and receding contact angles, is affected by electrowetting. The analysis reveals nine distinct regimes characterizing contact angle behavior, three of which arise only when a voltage is applied to the conductive liquid drop. As the square voltage is progressively increased, the theory elucidates how the drop occasionally undergoes regime transitions triggering jumps in the contact angle, possibly changing its hysteresis, or saturating it at a value weakly dependent on further voltage growth. To illustrate these phenomena and validate the theory, we confront its predictions with four data sets. A benefit of the theory is that it forsakes trial and error when designing textured surfaces with specific contact angle behavior.The figure below is the graphical abstract illustrating predictions of the calculations against the data set of Gupta, et al, Langmuir (2011).

As supporting information
of this paper on electrowetting theory, we provide two Matlab programs
that calculate contact angles and their regimes using the
first-principle method outlined in the article. They are Electrowetting.m and ElectroWettingKrupenkin.m . Click on their names to download.